00:00 - 00:00
Sourced from: https://www.chinaz.com/2023/0606/1531620.shtml
Tiedong Liu and Bryan Kian Hsiang Low, researchers from National University of Singapore recently introduced Goat, a fine-tuned LLaMA model that significantly outperforms GPT-4 on a range of arithmetic tasks.
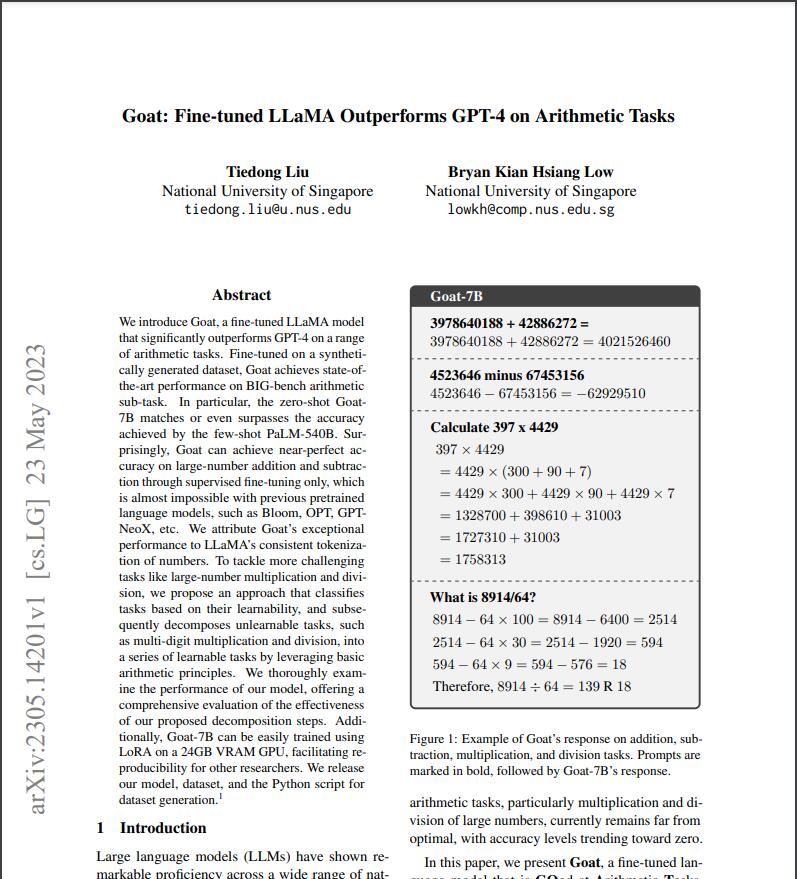
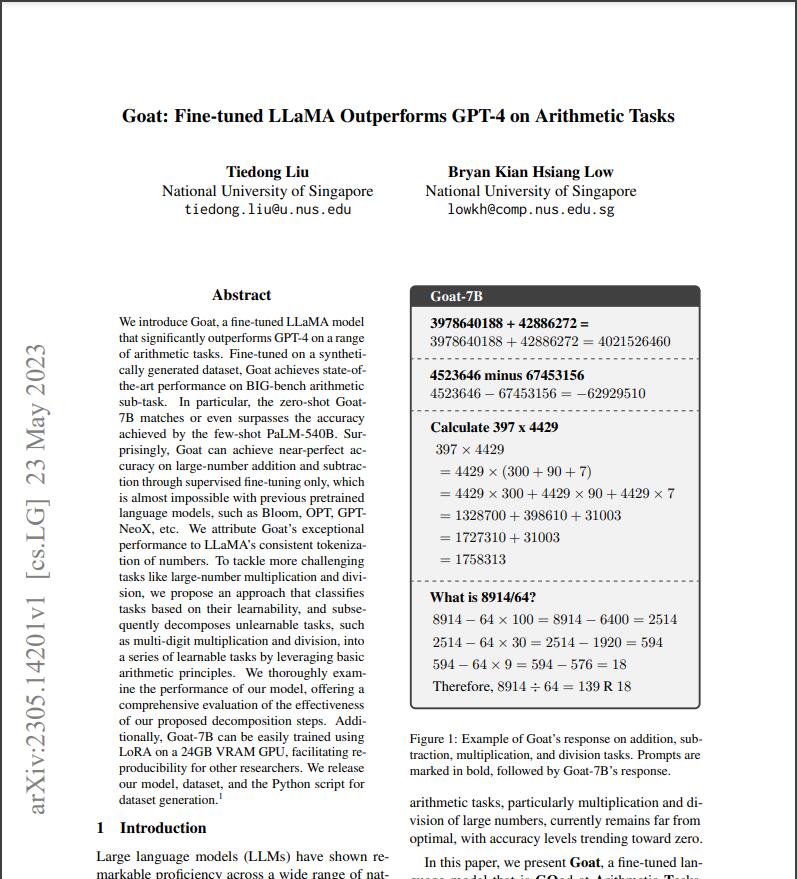
Fine-tuned on a synthetically generated dataset. Goat achieves state-of-the-art performance on BIG-bench arithmetic sub-task. In particular, the zero-shot Goat7B matches or even surpasses the accuracy achieved by the few-shot PaLM-540B.Surprisingly, Goat can achieve near-perfect ac- curacy on large-number addition and subtraction through supervised fine-tuning only, which is almost impossible with previous pretrained language models. such as Bloom, OPTGPT NeoX, etc.
The researchers attribute Goat’s exceptional performance to LLaMA's consistent tokenization of numbers. To tackle more challenging tasks like large-number multiplication and division, they propose an approach that classifies tasks based on their learnability and subsequently decomposes unlearnable tasks, such as multi-digit multiplication and division into a series of learnable tasks by leveraging basic arithmetic principles. They thoroughly examine the performance of their model offering a comprehensive evaluation of the effectiveness of our proposed decomposition steps.
Additionally, Goat-7B can be easily trained using LoRA on a 24GB VRAM GPU facilitating re-producibility for other researchers. The researchers release their model, dataset, and the Python script for dataset, and the Python script for dataset generation.